VIEW INDIA’S GENDER GAP REPORT RANKING AS A WARNING
TOPIC: (GS2) GOVERNANCE: THE HINDU
India ranks 131 out of 148 countries in the Global Gender Gap Report 2025 by the World Economic Forum, showing serious gaps in economic participation and women’s health. The report acts as a warning that gender equality must become a national development priority.
India’s Low Ranking Reflects Deeper Issues
- Despite its growing economy and technological growth, India remains behind in gender equality.
- The country’s weak position in economic participation and women’s health shows deep-rooted systemic failures.
Women’s Health and Survival Still Poor
- Skewed sex ratio at birth indicates persistent son preference in society.
- Women’s life expectancy has dropped below that of men.
- Reproductive care, nutrition, and primary healthcare for women, especially in rural and poor areas, are still inadequate.
- As per NFHS-5, about 57% of women (15–49 years) are anaemic, affecting their ability to study, work, or have healthy pregnancies.
Economic Participation Gap is Alarming
- India is 143rd in the Economic Participation and Opportunity subindex.
- Women earn less than one-third of what men earn and have low workforce participation.
- In 2015, McKinsey projected that closing the gender gap could add $770 billion to GDP, but this potential remains untapped in 2025.
Unpaid Care Work is a Hidden Burden
- Indian women spend nearly 7 times more time on unpaid household tasks than men.
- This work is not counted in national income data or addressed in most government budgets.
- Lack of support like childcare, elderly care services, and maternity benefits keeps women out of paid jobs.
Need for Policy Change and Investment
- Governments must recognise and account for unpaid care work in budgets and policies.
- Countries like Uruguay and South Korea have built care-based economies and can serve as examples.
- Time-use surveys and gender budgeting should become part of planning.
Demographic Challenges Ahead
- India is ageing; by 2050, nearly 20% of the population will be senior citizens, mostly older women.
- With declining fertility rates, fewer workers will support more dependents.
- Keeping women healthy and in the workforce is vital for sustaining economic growth.
Conclusion
India must treat gender equality as a development goal, not just a social issue. Without serious investments in women’s health, economic inclusion, and care infrastructure, the country risks stalling its own progress.
IMPOSING ANY LANGUAGE AS THE MEDIUM OF INSTRUCTION IS UNACCEPTABLE
TOPIC: (GS2) GOVERNANCE: THE HINDU
The debate on the medium of instruction in schools has resurfaced amid the Centre’s push for a three-language policy. Many fear this could undermine the growing public demand for English-medium education, especially among disadvantaged communities.
Background of the Language Debate
- The medium of instruction in Indian schools varies widely between states and over time.
- The BJP government’s efforts to promote the three-language formula have intensified this issue.
- There’s a clash between pedagogical research (favoring mother tongue) and social aspirations (favoring English).
Mother Tongue vs. English: The Dilemma
- Educational experts say children learn better in their first language during early years.
- However, in India, mother tongue identification is complex due to linguistic diversity.
- In 2014, the Supreme Court ruled that the state cannot force a particular language; children must have freedom of choice.
- Imposing one language can violate constitutional rights like freedom of expression and education.
Public Aspiration for English Education
- English is viewed as a tool for empowerment, especially among marginalized communities.
- States like Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu run aided English-medium schools.
- The demand is high, even in Hindi-speaking regions, but most government schools don’t meet it.
- Private English-medium schools, often costly and of poor quality, fill the gap.
Inequality in Access to English Education
- English opens doors to global job markets and social mobility.
- If state schools deny English education, only the rich can afford it — increasing the education divide.
- Education’s aim is equity, but language policies risk widening inequalities instead of bridging them.
Policy Implications
- English may not be ideal for early schooling, but access to it must be equitable.
- A balanced approach is needed — promote regional languages while also offering English as an option, especially in public schools.
THREE LANGUAGE POLICY
What is the Three Language Policy?
It recommends that students learn three languages in school:
- 1st Language: Mother tongue or regional language
- 2nd Language: English or Hindi
- 3rd Language: Any modern Indian or foreign language not covered above
When was it introduced?
- First proposed in the National Policy on Education, 1968
- Reaffirmed in the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 with a flexible approach.
Why was it introduced?
- To promote national integration, multilingualism, and cultural understanding
- Also aimed to balance regional languages with Hindi and English.
Controversies and Challenges:
- Southern states (like Tamil Nadu) oppose mandatory Hindi, favoring two-language policy
- Implementation varies by state boards and CBSE/ICSE
- Debate over language imposition vs. language choice
Conclusion
Language policy should focus on empowering the most disadvantaged, not limiting their choices. Ensuring access to English education is key to equal opportunities in a globalizing world.
ED RAIDS IN U.S. DONKEY ROUTE CASE
TOPIC: (GS2) INDIAN POLITY: THE HINDU
The Enforcement Directorate (ED) has carried out fresh raids in Punjab and Haryana as part of its investigation into a human trafficking and money laundering racket linked to the illegal ‘Donkey Route’ used to enter the United States.
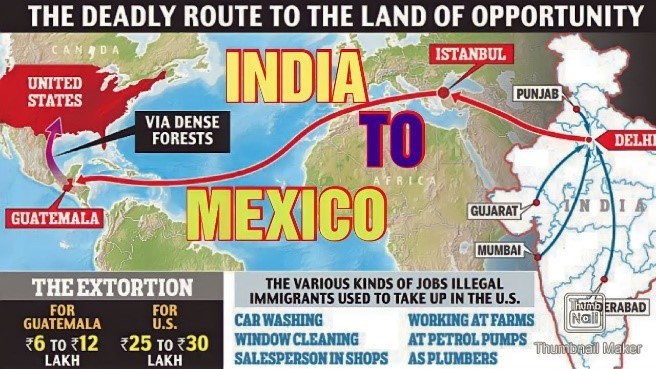
What is the Donkey Route?
- The “Donkey Route” refers to an illegal method of migration where people are smuggled across multiple international borders, often on foot or using dangerous jungle and sea paths.
- The route commonly passes through countries in South and Central America like Brazil, Ecuador, Guatemala, and Mexico, eventually leading to the U.S. border.
- Migrants often pay ₹45–50 lakh to traffickers, who promise legal travel but instead send them through unsafe paths.
Details of ED’s Investigation
- The ED conducted raids in Mansa (Punjab) and Kurukshetra and Karnal (Haryana).
- This follows earlier searches in Amritsar, Sangrur, Patiala, Moga, and Ambala.
- The probe is based on 17 FIRs filed in Punjab and Haryana against travel agents and middlemen.
- Victims were tricked into believing they would fly legally to the U.S.
Modus Operandi of Traffickers
- Agents in India collaborated with “donkers” (human smuggling agents) abroad.
- Victims were forced to cross multiple countries illegally.
- Families were blackmailed into paying extra during the journey.
Recent Developments
- The NIA arrested two traffickers in Himachal Pradesh and Delhi, linked to Gagandeep Singh, previously arrested for trafficking to the U.S.
- Statements from deported migrants helped in tracking the network.
Conclusion
The Donkey Route poses a serious security, humanitarian, and economic concern, as traffickers exploit vulnerable people with false promises of better life abroad. Strict enforcement and awareness are essential.
AI AND THE FUTURE OF INDIAN MANUFACTURING
TOPIC: (GS3) ECONOMY: THE HINDU
AI is reshaping India’s manufacturing sector by improving efficiency, reducing waste, and enabling intelligent automation. The government’s ₹10,372 crore AI Mission and rising industrial adoption mark a major shift in how India produces and competes globally.
How AI is Changing Manufacturing
- AI is now integrated into every level of factories, from assembly lines to logistics.
- It helps increase production speed, reduces machine downtime, and improves decision-making through real-time data.
- Predictive maintenance powered by AI can cut equipment failures by nearly 30%.
Technology Backbone
- IoT sensors and edge computing allow real-time responses and machine-level control.
- Cloud platforms scale up data storage, model training, and integration across multiple locations.
- AI connects with ERP, supply chains, and other systems through APIs.
AI’s Broader Impact
- Drives cost savings, quality control, and energy efficiency.
- Enables customised product design and faster innovation using generative AI.
- Helps India move toward becoming a global manufacturing hub.
Challenges Ahead
- High integration costs, shortage of skilled talent, and data governance concerns.
- Many firms are still cautious due to AI model unpredictability and lack of transparency.
Way Forward
- Develop AI-Specific Industrial Policy and Skilling Framework: Introduce a dedicated National AI Strategy for Manufacturing, aligned with Make in India and Industry 4.0 goals.
- Integrate AI-related courses into technical education, ITIs, and MSME skilling programs to create a future-ready workforce.
- Strengthen Digital Infrastructure and Support MSMEs: Provide financial incentives and infrastructure support (like subsidised cloud access, edge computing, IoT integration) for AI adoption by MSMEs, which form the backbone of Indian industry.
- Promote Responsible AI and Public-Private Collaboration: Establish regulatory frameworks for ethical AI use, focusing on data security, transparency, and accountability.
Conclusion
AI offers a chance to build smarter and globally competitive factories. With the right investment and strategy, India can lead the next phase of the industrial revolution.
U.S. SANCTIONS ON UN OFFICIAL
TOPIC: (GS2) INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS: THE HINDU
The United States has imposed sanctions on Francesca Albanese, the UN Special Rapporteur on Palestinian Territories, for her critical reports on Israel’s actions in Gaza, triggering international concern over U.S. interference in UN mandates.
Background of the Issue
- Francesca Albanese, a UN-appointed expert, monitors human rights violations in the occupied Palestinian territories.
- She has criticized Israel’s military actions in Gaza, calling them extreme and potentially genocidal.
- Her report in June 2025 called for prosecution of companies funding the war.
Nature of U.S. Sanctions
- Announced by U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio.
- May include visa bans, travel restrictions, and freezing of assets.
- The move is linked to her support for the International Criminal Court (ICC), which is investigating war crimes.
Global Criticism
- The UN Human Rights Council condemned the U.S. action as a dangerous precedent.
- Critics say this undermines international institutions like the UN, ICC, and ICJ.
- The U.S. claims she acted without consent from Israel and the U.S., but this has no legal basis under international law.
Larger Context
- The U.S. focus on an individual UN expert appears disproportionate, especially amid rising civilian deaths in Gaza.
- Many nations, including India at the BRICS summit, have expressed concern over Israel’s actions.
UNITED NATIONS (UN)
- Establishment: The United Nations was founded on 24 October 1945 after World War II to promote peace and international cooperation. 51 countries were original members; today it has 193 member states.
- Principal Organs: The UN has 6 main organs, including the UN General Assembly, UN Security Council, UN Secretariat, Economic and Social Council, International Court of Justice, and Trusteeship Council.
- India and the UN: India is a founding member of the UN and has consistently contributed to UN Peacekeeping Missions, being one of the largest troop contributors.
- UN Headquarters and Funding: The UN headquarters is in New York, USA. The top 5 contributors to the UN regular budget (as of 2024): USA, China, Japan, Germany, and the UK.
Conclusion
Rather than targeting a UN official, the U.S. should work towards an immediate ceasefire in Gaza. Silencing critics only harms global accountability and diplomacy.
ISLANDS PROTECTION ZONE (IPZ) NOTIFICATION, 2011
TOPIC: (GS3) ENVIRONMENT: PIB
The Union Environment Ministry has issued an amendment to the IPZ 2011 Notification, extending the validity of environment clearances from 7 to 10 years, amid rising tourism and development activities in India’s island territories.
What is IPZ Notification?
- Issued under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- Aims to regulate development activities and preserve ecosystems in Andaman & Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep.
- Seeks to protect coral reefs, mangroves, beaches, and marine biodiversity.
Key Amendment
- Validity of environmental clearance for projects has been increased to 10 years (earlier 7 years).
- Comes as major projects like the ₹81,800 crore Great Nicobar Holistic Development Project (port, airport, power plant, roads, etc.) are being undertaken.
IPZ VS CRZ
- CRZ (Coastal Regulation Zone): Applies to mainland India.
- IPZ: Specifically applies to islands like Lakshadweep and Andaman & Nicobar.
Overview of CRZ Rules
- First notified in 1991, revised in 2011 and 2019.
- Divides coastal land into four zones (CRZ-I to CRZ-IV).
- CRZ-I: Most ecologically sensitive.
- CRZ-II: Developed urban areas near the coast.
- CRZ-III: Rural and relatively undisturbed areas.
- CRZ-IV: Water area up to 12 nautical miles from the coast.
- Controls construction, tourism, industry, and other activities in these zones.
Conclusion
As India expands infrastructure on islands, balancing development and ecology is essential. The updated IPZ rules aim to streamline project timelines while still protecting fragile coastal ecosystems.
ZONAL COUNCILS OF INDIA
TOPIC: (GS2) INDIAN POLITY: PIB
The 27th meeting of the Eastern Zonal Council was recently chaired by the Union Home Minister in Ranchi, Jharkhand, to discuss key regional and inter-state issues.
What are Zonal Councils?
- Zonal Councils are statutory bodies formed under the States Reorganisation Act, 1956.
- The Act grouped India into five zones: Northern, Central, Eastern, Western, and Southern—each with a separate zonal council.
Members of Zonal Councils
- Union Home Minister is the Chairman of all Zonal Councils.
- Chief Ministers of all states in the zone.
- Two ministers from each participating state.
- Administrators of Union Territories in that zone.
- Each Chief Minister becomes Vice-Chairperson of the council in rotation for one year.
Purpose and Role
- They serve as discussion platforms to encourage cooperation between the Centre and States.
- Discuss matters related to:
- Economic and social development
- Linguistic and minority rights
- Interstate transport and infrastructure
- Border disputes and internal security
- They offer advice and suggestions but have no legislative powers.
North-Eastern Council
- Created under a separate North-Eastern Council Act, 1971.
- Includes eight states: Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh, and Sikkim.
- Focuses on development planning and coordination in the northeast.
Standing Committees
- Each zonal council has a Standing Committee led by the Chief Secretaries of the states for regular coordination.
Conclusion
Zonal Councils play a vital role in promoting cooperative federalism by creating a structured dialogue between states and the Union on shared challenges and development goals.
DHAMMACHAKRA PRAVARTANA DIVAS
TOPIC: (GS1) INDIAN CULTURE AND HERITAGE: PIB
The International Buddhist Confederation (IBC), with support from the Ministry of Culture, observed Ashadha Purnima as Dhammachakra Pravartana Divas, marking Buddha’s first sermon after enlightenment.
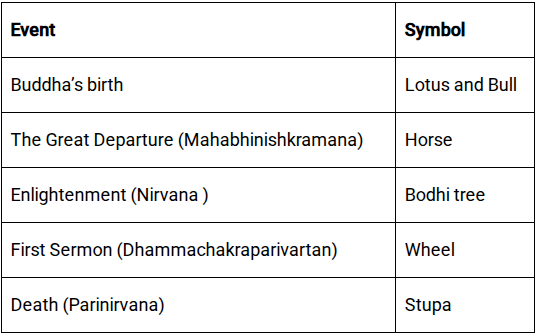
What is Dhammachakra Pravartana Divas?
- Observed on the full moon of the Ashadha month, it celebrates the day when Gautama Buddha gave his first sermon.
- The sermon was delivered at Deer Park in Sarnath, near Varanasi, to five ascetic followers (Pañcavargiya).
- It marks the “Turning of the Wheel of Dharma”, the beginning of the spread of Buddha’s teachings.
Cultural and Spiritual Importance
- Considered the second holiest day for Buddhists after Buddha Purnima.
- It also begins the Varsha Vassa period—when monks observe rainy season retreats for meditation and self-restraint.
- The day promotes non-violence, compassion, and moral discipline.
Names in Other Countries
- Known as Esala Poya in Sri Lanka.
- Celebrated as Asanha Bucha in Thailand.
Conclusion
Dhammachakra Pravartana Divas holds great historical and spiritual value, reminding the world of Buddha’s first message of truth and compassion.
