Table of Contents
ToggleThe Early Earth Environment
Before life could emerge, the planet had to undergo significant physical changes. Around 4.6 billion years ago, the Earth was a molten mass. By 4 billion years ago, the surface had cooled enough for the Hydrosphere to form.
- Primordial Soup: The early oceans were rich in organic compounds, often referred to as a “primordial soup.”
- Reducing Atmosphere: The early atmosphere was reducing, meaning it lacked free oxygen and was composed of methane, ammonia, water vapor, and hydrogen.
- Energy Sources: Intense UV radiation (due to the lack of an Ozone layer), lightning, and volcanic heat provided the energy for chemical reactions.
Chemical Evolution (Chemosynthesis)
Modern science, following the Oparin-Haldane Hypothesis, suggests that life originated through a series of chemical reactions.
- Formation of Monomers: Simple inorganic molecules reacted to form amino acids, sugars, and nucleotides.
- Polymerization: These monomers joined to form complex polymers like proteins and nucleic acids (RNA/DNA).
- Protobionts: These were non-living aggregates of organic molecules surrounded by a membrane-like structure, exhibiting some characteristics of life like metabolism.
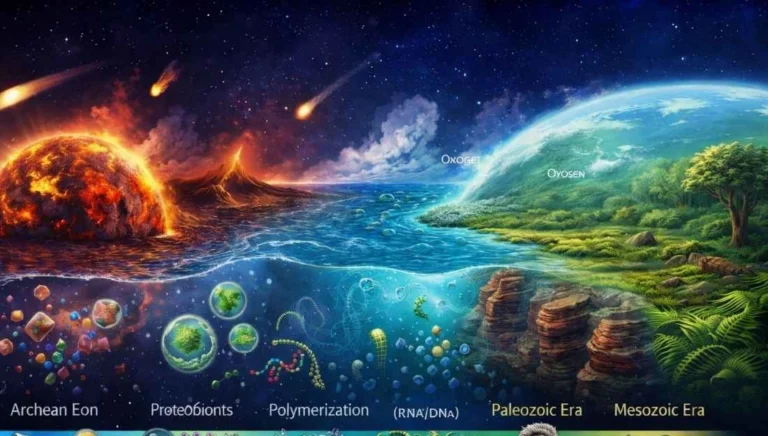

Biological Evolution and the First Life Forms
The transition from complex chemistry to biology occurred roughly 3.5 to 3.8 billion years ago.
- Anaerobic Heterotrophs: The first life forms were likely unicellular bacteria that lived in the absence of oxygen and consumed organic molecules from their surroundings.
- Chemoautotrophs: Later, organisms evolved that could produce their own energy using chemical reactions from deep-sea hydrothermal vents.
- Cyanobacteria: The most significant milestone was the evolution of blue-green algae. These were the first photoautotrophs capable of oxygenic photosynthesis
The Great Oxidation Event (GOE)
The emergence of cyanobacteria fundamentally changed the Earth’s Physical Geography.
- Oxygenation of Oceans: Initially, the oxygen produced was used to oxidize dissolved iron in the oceans, creating Banded Iron Formations (BIFs).
- Atmospheric Oxygen: Once the “sinks” were full, oxygen began to accumulate in the atmosphere roughly 2.4 billion years ago.
- Formation of the Ozone Layer: Atmospheric oxygen led to the creation of the Ozone (O3) layer, which shielded the Earth from harmful UV rays, allowing life to migrate from the oceans to land.



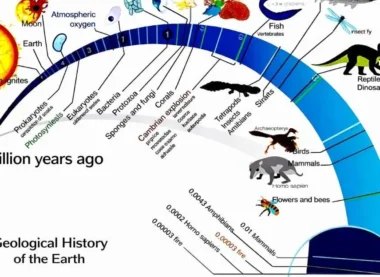
Geological Time Scale and Life
| Era/Eon | Biological Milestone |
| Archean Eon | Emergence of Prokaryotes (Bacteria). |
| Proterozoic Eon | Rise of Eukaryotes (complex cells) and Multicellular life. |
| Paleozoic Era | The Cambrian Explosion; colonization of land by plants and amphibians. |
| Mesozoic Era | Dominance of Reptiles and Gymnosperms. |
| Cenozoic Era | Dominance of Mammals and Angiosperms. |
Key Theories for UPSC
- Panspermia: The hypothesis that life exists throughout the Universe and was brought to Earth by meteorites or comets.
- Hydrothermal Vent Theory: Suggests life began in the mineral-rich, high-pressure environments of the deep ocean floor.
- RNA World Hypothesis: Proposes that RNA was the first self-replicating molecule before DNA and proteins.
Crucial Concepts for Mains
- Co-evolution: Life did not just evolve on Earth; it co-evolved with the Earth. The transition from a reducing atmosphere to an oxidizing atmosphere is the best example of life altering the physical planet.
- Extremophiles: The study of organisms living in extreme conditions today helps scientists understand how life survived on the harsh early Earth.
UPSC Prelims: PYQs & Practice Questions
Previous Year Questions (Prelims)
Question 1 (UPSC 2012)
Q: Which of the following is/are cited by the scientists as evidence/s for the continued expansion of universe?
1. Detection of microwaves in space.
2. Observation of redshift phenomenon in space.
3. Movement of asteroids in space.
4. Occurrence of supernova explosions in space.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) None of the above
Answer: (a)
Explanation: Detection of Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMBR) and observation of redshift are key evidences supporting an expanding universe. Asteroid movement and supernovae are local/stellar phenomena and do not directly establish universal expansion.
Question 2 (General Science)
Q: Which of the following was/were NOT present in the Earth’s atmosphere at the time of the origin of life?
1. Oxygen
2. Methane
3. Ammonia
4. Hydrogen
Select the correct answer:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 2, 3 and 4
(d) All of the above
Answer: (a)
Explanation: The early atmosphere was reducing and lacked free oxygen (O₂). Oxygen accumulated much later after the Great Oxidation Event driven by cyanobacteria, while methane, ammonia, and hydrogen were part of the early gaseous mix.
Practice Questions (Prelims)
Question 1
Q: With reference to the ‘RNA World Hypothesis’, consider the following statements:
1. It suggests that RNA was the first genetic material to store information and catalyze chemical reactions.
2. RNA is more stable than DNA, which led to its dominance in early life forms.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (a)
Explanation: Statement 2 is incorrect. DNA is chemically more stable than RNA due to its double-stranded structure and the presence of thymine instead of uracil. Hence, DNA eventually became the primary genetic reservoir.
UPSC Mains – Previous Year & Practice Questions
Previous Year Questions (Mains)
Great Oxidation Event
Question: Explain the phenomenon of the ‘Great Oxidation Event’ and its significance in the evolution of life on Earth. (Applied Geography/Science)
Extremophiles & Astrobiology
Question: How does the study of extremophiles help in understanding the possibility of life on other planets? (Science & Tech)
Cambrian Explosion
Question: Discuss the significance of the Cambrian Explosion in the geological history of the Earth. (Geography)
Atmospheric Evolution
Question: The Earth’s atmosphere has changed significantly since its formation. Illustrate the role of biological organisms in this transformation. (Physical Geography)
Big Bang Theory
Question: What is the ‘Big Bang Theory’? How does it explain the origin of the universe and subsequent formation of Earth? (Basic Science/Geography)
Mains Practice Questions
Reducing to Oxidizing Atmosphere
Question: “The transition from a reducing atmosphere to an oxidizing one was the single most important geochemical event in Earth's history. Evaluate.” (150 words)
Oparin–Haldane & Miller–Urey
Question: “Explain the Oparin-Haldane hypothesis. To what extent did the Miller-Urey experiment provide empirical evidence for this theory?” (250 words)
Panspermia & Space Missions
Question: “Discuss the ‘Panspermia’ theory in the context of recent space missions like ISRO’s Shukrayaan or NASA’s Perseverance.” (150 words)
The Origin of Life: A Comprehensive UPSC Guide
What is the "Primordial Soup"?
It is a term coined by J.B.S. Haldane describing the early Earth’s oceans. It was a hot, dilute soup of organic molecules (amino acids, sugars) formed from inorganic precursors through energy from lightning and UV rays
Why did life start in the ocean and not on land?
Early Earth lacked an Ozone layer. The land was bombarded by lethal UV radiation. Water acted as a natural shield, protecting the first delicate organic molecules and cells.
What are Banded Iron Formations (BIFs)?
These are sedimentary rocks consisting of alternating layers of iron oxides and chert. They are crucial “geological clocks” proving that early Cyanobacteria were producing oxygen, which reacted with dissolved iron in the ocean before entering the atmosphere.
What is the difference between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes in the Geological Time Scale?
Prokaryotes (simple cells without a nucleus, like bacteria) appeared first in the Archean Eon. Eukaryotes (complex cells with a nucleus) appeared later in the Proterozoic Eon, likely through endosymbiosis (one cell engulfing another).
Is the "RNA World" theory widely accepted?
Yes, it is the leading hypothesis because RNA can both store genetic information (like DNA) and act as an enzyme (like proteins), solving the “chicken and egg” problem of which came first.