Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to Early Hypotheses
The quest to understand the Origin of the Earth has led to numerous scientific and philosophical theories. In the early stages, these were divided into monistic (single parent) and dualistic (two parents) theories.
The Nebular Hypothesis
- Immanuel Kant, a German philosopher, provided one of the earliest popular arguments.
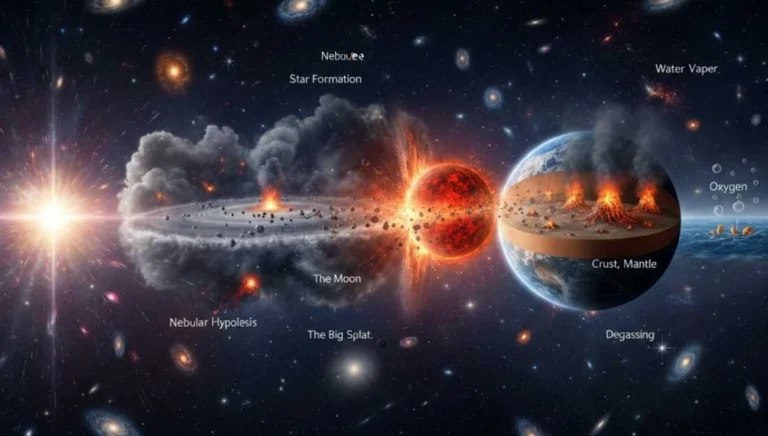
- Laplace (1796) revised this into the Nebular Hypothesis, which suggests that planets formed from a rotating cloud of material (nebula) associated with a young sun.
- Revised Nebular Hypothesis: In 1950, Otto Schmidt (Russia) and Carl Weizascar (Germany) proposed that a solar nebula consisting of hydrogen, helium, and dust surrounded the sun.
- Through the friction and collision of particles, a disk-shaped cloud formed, and planets were created via the process of accretion.
Binary Theories and Wandering Stars
- Chamberlain and Moulton (1900) proposed that a wandering star approached the sun, causing a cigar-shaped extension of material to separate from the solar surface.
- As the star moved away, this material condensed into planets while revolving around the sun.
- This “tidal” argument was supported by Sir James Jeans and Sir Harold Jeffrey.
Modern Theories: The Big Bang
Modern science focuses more on the Origin of the Universe rather than just the Earth. The most widely accepted theory is the Big Bang Theory, also known as the Expanding Universe Hypothesis.
The Expanding Universe
- Edwin Hubble provided evidence in 1920 that the universe is expanding, with galaxies moving further apart over time.
- Stages of the Big Bang:
- Singularity: Initially, all matter existed in a “tiny ball” with infinite temperature and infinite density.
- The Explosion: Around 13.7 billion years ago, this tiny ball exploded violently, leading to a rapid expansion that continues today.
- Cooling and Matter: Within 3 minutes of the Big Bang, the first atoms began to form. Within 300,000 years, temperature dropped to 4,500K, giving rise to atomic matter and making the universe transparent
Stages of the Big Bang:
- Singularity: Initially, all matter existed in a “tiny ball” with infinite temperature and infinite density.
- The Explosion: Around 13.7 billion years ago, this tiny ball exploded violently, leading to a rapid expansion that continues today.
- Cooling and Matter: Within 3 minutes of the Big Bang, the first atoms began to form. Within 300,000 years, temperature dropped to 4,500K, giving rise to atomic matter and making the universe transparent.
Star Formation and Planetesimals
The formation of Earth is intrinsically linked to the birth of stars and the subsequent development of planets.
Formation of Stars
- Nebulae: Distribution of matter and energy was not even. Gravitational differences led to the accumulation of gas clouds called nebulae.
- Gaseous Bodies: Within these nebulae, localized clumps of gas grew into dense, rotating gaseous bodies, eventually becoming stars roughly 5-6 billion years ago.
Formation of Planets
The development of planets like Earth occurred in three distinct stages:
- Gravity and Cores: Gravitational force within gas clouds led to the formation of a core and a rotating disk of gas and dust.
- Planetesimals: Matter condensed into small, rounded objects called planetesimals through the process of cohesion.
- Accretion: These planetesimals collided and merged due to gravitational attraction, forming larger bodies known as planets
The Solar System and the Moon
Our Solar System consists of 8 planets, 63 moons, and millions of smaller bodies like asteroids and comets.
Terrestrial vs. Jovian Planets
- Terrestrial Planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars): These are “Earth-like,” small, and made of rock and metals with high densities.
- Jovian Planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune): These are “gas giants,” much larger, and have thick atmospheres mostly made of hydrogen and helium.
- Why the difference? Terrestrial planets were too close to the sun for gases to condense, and intense solar winds stripped away their primary atmospheres.
The Origin of the Moon
- The Big Splat: Scientists believe the moon formed roughly 4.44 billion years ago when a body the size of Mars collided with Earth.
- This collision blasted a portion of Earth into space, which then orbited the Earth and condensed into the Moon.
Evolution of the Earth's Structure
Early Earth was a volatile, barren, and hot entity with a thin atmosphere of hydrogen and helium.
Lithosphere and Differentiation
- As the Earth’s density increased, its internal temperature rose.
- Primordial Differentiation: Heavier materials (like iron) sank to the center, while lighter materials (like silicate) moved toward the surface.
- This resulted in the Earth’s layered structure: Crust, Mantle, Outer Core, and Inner Core.
Evolution of Atmosphere and Hydrosphere
The Earth’s atmosphere evolved through three stages:
- Loss of Primordial Atmosphere: Solar winds stripped away the initial hydrogen and helium.
- Degassing: Volcanic eruptions released water vapor, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and methane from the interior.
- Photosynthesis: Early life modified the atmosphere by increasing oxygen levels.
UPSC Prelims: PYQs & Practice Questions
Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Question 1 (2012)
Q: Which of the following is/are cited by the scientists as evidence/evidences for the continued expansion of the universe?
1. Detection of microwaves in space.
2. Observation of redshift phenomenon in space.
3. Movement of asteroids in space.
4. Occurrence of supernova explosions in space.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Options:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) None of the above
Answer: (a)
Explanation: The Big Bang theory (Expanding Universe Hypothesis) is supported by the observation of redshift (showing galaxies moving away) and the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation, which is the remnant heat from the Big Bang. The movement of asteroids and supernova explosions are localized events and do not provide evidence for the expansion of the entire universe.
Prelims Practice Questions
Question 1
Q: Consider the following statements regarding the "Nebular Hypothesis":
1. It was originally proposed by the mathematician Laplace and later revised by Immanuel Kant.
2. It suggests that planets were formed out of a cloud of material associated with a youthful, slowly rotating sun.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Options:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (b)
Explanation: While both Kant and Laplace contributed to the theory, it was Immanuel Kant who first proposed it, and Laplace later revised it in 1796. The theory explains that planets formed from a rotating nebula associated with a young sun.
Question 2
Q: Why are the inner planets (Terrestrial) rocky while the outer planets (Jovian) are mostly gaseous?
1. Terrestrial planets were formed in the close vicinity of the parent star where it was too warm for gases to condense.
2. The solar wind was most intense nearer the sun, blowing off lots of gas and dust from terrestrial planets.
3. The terrestrial planets are smaller and their lower gravity could not hold the escaping gases.
Select the correct answer:
Options:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (d)
Explanation: All three factors contributed. The proximity to the sun prevented gas condensation, intense solar winds stripped the primary atmospheres, and the low gravity of smaller terrestrial planets meant they couldn't retain lighter gases like hydrogen and helium.
UPSC Mains – Previous Year & Practice Questions
Previous Year Mains Questions
Terrestrial vs Jovian Planets (2021)
Question: Differentiate between the causes of the formation of the terrestrial and Jovian planets. (150 words)
Continental Drift Theory (2013)
Question: What do you understand by the theory of 'Continental Drift'? Discuss the prominent evidence in its support. (Note: While this relates to Earth's evolution, it is often linked to the Origin topic in the syllabus).
Big Bang Theory
Question: Explain the "Big Bang Theory" regarding the origin of the Universe.
Differentiation of the Earth
Question: Describe the process of 'Differentiation' in the context of the Earth's layered structure.
Evolution of the Atmosphere
Question: How did the Earth's atmosphere evolve from its primordial stage to the present one?
Mains Practice Questions (3)
Formation of the Moon
Question: "The formation of the Moon was a result of a 'Big Splat'." Elaborate on this theory and its impact on Earth's early characteristics. (250 words)
Nebular Hypothesis
Question: Discuss the 'Nebular Hypothesis' and explain how modern versions of this theory differ from early 18th-century versions. (150 words)
Evolution of Earth's Atmosphere
Question: Analyze the role of volcanic degassing and photosynthesis in the evolution of the Earth’s present-day atmosphere. (250 words)
The Origin of the Earth: A Comprehensive UPSC Guide - FAQs
What is the age of the Earth and the Universe?
The Universe is approximately 13.7 billion years old, while the Earth formed about 4.6 billion years ago.
What are 'Planetesimals'?
They are small, rounded objects formed in the early solar system through the process of cohesion and gravitational attraction within a rotating disk of gas. These planetesimals eventually collided to form larger planets.
What does 'Degassing' mean in Physical Geography?
Degassing is the process by which gases were released from the interior of the Earth through volcanic eruptions during its early cooling stages. This process was fundamental in forming the early atmosphere, releasing water vapor, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide.
Is the Big Bang the only theory for the Origin of the Universe?
While the Big Bang is the most accepted “Expanding Universe” model, there was also the Steady State Theory proposed by Hoyle, which suggested the universe remained the same at any point in time. However, current evidence largely supports the Big Bang.
What is 'Differentiation'?
It is the process where, due to heating and gravity, heavier materials (like iron) sank to the center of the Earth to form the core, while lighter materials moved toward the surface to form the crust.

