INDIA’S ROLE IN THE GLOBAL PRECISION MEDICINE MARKET
TOPIC: (GS3) ECONOMY: THE HINDU
India is emerging as an important centre for research, innovation, and affordable biotechnology solutions. With rising non-communicable diseases (NCDs) and a diverse genetic pool, India is positioning itself as a major contributor to personalised healthcare.
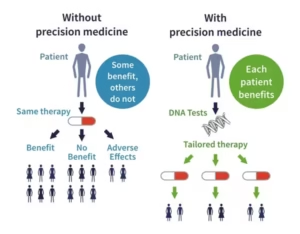
What is Precision Medicine?
- Precision medicine focuses on tailoring medical treatment to an individual’s genetic characteristics, molecular profile, and disease markers.
- It shifts healthcare from broad prescriptions to targeted therapy, improving diagnosis, reducing side effects, and increasing treatment success.
Technologies Driving Precision Biotherapeutics
- Genomic & Proteomic Mapping: Helps identify genetic mutations and disease-causing protein variations.
- Gene Editing Tools (e.g., CRISPR-Cas9): Used to correct defective genes responsible for inherited conditions like sickle-cell disease.
- mRNA and Nucleic Acid Therapies: Guide cells to produce or block specific proteins; widely used in COVID-19 vaccines.
- Monoclonal Antibodies and Biologics: Target specific disease pathways, especially in cancer and autoimmune disorders.
- AI-Based Drug Development: Machine learning accelerates molecule screening and drug discovery.
Global Market Landscape
- The precision medicine market was valued at around USD 12 billion in 2023 and is projected to double by 2027.
- Growth is driven by advances in genome sequencing, increasing NCD burden, AI integration, and rising pharma investments.
- The US, Europe, and China lead the market, but countries like India and Brazil are becoming competitive due to lower costs and expanding research capacity.
India’s Emerging Role
- India faces a heavy burden of NCDs, making personalised treatment models crucial.
- India’s genetic diversity provides a unique environment for testing and developing precision therapies.
- The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has prioritised precision biotherapeutics under the BioE3 policy.
- Genomic initiatives like GenomeIndia and IndiGen are building population-specific gene databases to improve drug response for Indian patients.
Key Challenges
- Regulatory Vacuum: Lack of a unified law for gene, cell, and molecular therapies.
- High Costs: Advanced therapies remain unaffordable for most Indians.
- Manufacturing Limitations: Shortage of large-scale biologics and cell-therapy production facilities.
- Ethical Concerns: Genomic data sharing requires strong safeguards and privacy regulations.
Opportunities for India
- Strengthen biomanufacturing under Make in India for biotech.
- Encourage public–private partnerships in R&D and clinical trials.
- Develop clear regulations to build global trust.
- Expand genomic datasets to enable personalised drug design for Indian populations.
Conclusion
With its scientific talent, expanding biotech ecosystem, and genetic diversity, India is well placed to grow into a global centre for affordable precision medicine. Addressing regulatory, ethical, and manufacturing gaps will be vital to realising this potential.
INDIA’S EV PUSH AMID CHINESE EXPORT RESTRICTIONS ON HREES
TOPIC: (GS3) ECONOMY: THE HINDU
China’s new export restrictions on key heavy rare earth elements used in EV motors have In response, Indian start-ups like Simple Energy and Chara Technologies are building rare-earth-free motors to boost self-reliance and strengthen India’s EV ecosystem.
China’s Rare Earth Export Controls
- April 2025: China restricted exports of seven HREEs—samarium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, lutetium, scandium, and yttrium.
- October 2025: Curbs were widened to include holmium, europium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, and related magnetic materials.
- Reason: These actions are linked to the prolonged US–China trade conflict, raising vulnerabilities for global EV manufacturers.
- India’s Dependence: India imported 2,270 tonnes of rare earths in 2023–24, a 23% rise since 2019–20, with 65% sourced from China.

Indigenous Technology in India
- Innovation: Developed a heavy rare-earth-free Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM).
- Uses redesigned magnet compositions (iron, neodymium, boron, praseodymium, holmium alternatives). Applies proprietary thermal, torque, and magnetic field optimisation software.
- Performance: Achieves around 99.5% efficiency compared to conventional PMSM motors.
- Handling restrictions: Even after holmium became restricted, the company prepared holmium-free designs and built adequate stock.
- Market impact: All its EVs now use motors free of restricted HREEs; recorded 1,050 sales in October 2025, a 215% YoY increase.
Chara Technologies
- Innovation: Built India’s first magnet-free SynRM (Synchronous Reluctance Motor) designed for EVs.
- Breakthrough: Traditionally SynRM motors were suited only for low-speed industry use. Chara redesigned them for high speeds and variable loads.
- Advantages: Comparable power and torque to PMSM units, with a modest 16% size increase.
- Current use: Deployed in agriculture and industrial equipment, with entry into the EV three-wheeler market expected soon.
Strategic Importance for India
- Supply-chain resilience: Reduces dependence on Chinese rare earths.
- Technological sovereignty: Encourages domestic R&D, innovation, and IP creation.
- Geopolitical safety: Lessens India’s exposure to critical mineral weaponisation.
- Industry momentum: Major firms like Ola Electric and TVS are exploring rare-earth-free technologies (e.g., ferrite motors).
Challenges Ahead
- Matching size, efficiency, and performance of PMSM motors.
- Ensuring consistent supply and affordability of alternative magnet alloys.
- Encouraging manufacturers to adopt new indigenous motor designs.
- Limited domestic mining, separation, and refining capacity for rare earths.
Way Forward
- Strengthen critical mineral exploration under the National Mineral Exploration Policy.
- Boost R&D through PLI schemes, innovation grants, and Start-up India support.
- Develop a domestic magnet manufacturing ecosystem (ferrite and alternative alloys).
- Promote scaling through EV policies, fleet procurement, and demand aggregation.
- Partner with nations like Japan, Australia, and the US for mineral and technology diversification.
Conclusion
India’s rare-earth-free EV motor innovations are helping reduce dependence on China while improving supply-chain security. These advancements support Atmanirbhar Bharat, enhance energy independence, and strengthen India’s EV ecosystem.
FLEXIBLE INFLATION TARGETING (FIT) IN INDIA
TOPIC: (GS3) ECONOMY: THE HINDU
India’s Flexible Inflation Targeting (FIT) framework, is due for review in March 2026, prompting debate over whether the current target remains suitable amid frequent supply shocks and changing economic conditions.
Why Inflation Management Matters
- Inflation acts like a regressive tax, hurting low-income households most as their incomes do not adjust quickly to rising prices.
- Persistent high inflation distorts investment decisions, reduces savings incentives, and creates uncertainty in long-term planning.
- Earlier committees (e.g., Chakravarty Committee, 1985) suggested a 5% comfort level, but macroeconomic structures have transformed since then.
- The end of automatic monetisation of deficits in 1994 and adoption of FIT in 2016 gave RBI stronger autonomy and improved policy discipline.
Features of India’s FIT Framework
- Central target: 4% CPI inflation with a 2% band on either side.
- Target variable: Headline CPI, chosen because food and fuel have a major impact on household spending in India.
- The band gives flexibility to accommodate supply shocks, while still anchoring expectations.
- Despite global crises, inflation has generally stayed within or close to the tolerance zone, strengthening credibility.
Headline vs Core Inflation
- Headline inflation captures the full range of price movements, including food and energy—important in India’s consumption pattern.
- Core inflation reflects underlying demand pressures but may miss crucial supply-side dynamics.
- A rise in relative prices (e.g., only food or only wages) does not create sustained inflation unless accompanied by excess liquidity—consistent with classical monetary theory.
What Long-Term Data Indicates
- RBI’s recent analysis (1991–2023, excluding COVID years) finds a non-linear inflation–growth relationship.
- Growth improves as inflation rises but only up to about 4%, after which higher inflation reduces economic expansion.
- This suggests that 4% is close to India’s growth-maximising inflation rate.
How Flexible Should the Band Be?
- FIT has allowed the RBI to deal with repeated supply shocks.
- But inflation staying near the upper limit for long periods may dilute credibility.
- The framework helps avoid earlier episodes of fiscal dominance when deficits were monetised automatically.
Determining an Acceptable Inflation Level
- The Phillips Curve suggests richer economies tolerate slightly higher inflation; however, India faces:
- frequent food and fuel shocks,
- climate-linked volatility,
- imported inflation, and limited fiscal space.
- Maintaining the 4% target requires strong expectation anchoring to avoid wage-price spirals.
Conclusion
India’s FIT framework has helped anchor inflation and enhance policy credibility, with evidence suggesting that a 4% target still suits current economic conditions. Strengthening shock management, supply-side measures, and fiscal–monetary balance will be vital for maintaining stable growth ahead.
BIRSA MUNDA AND TRIBAL ASSERTION
TOPIC: (GS1) INDIAN CULTURE: THE HINDU
Birsa Munda is in the news as his birth anniversary is being commemorated along with the conclusion of Janjatiya Gaurav Varsh (2021–24), highlighting the government’s focus on honoring tribal heritage.
About Janjatiya Gaurav Divas
- Birsa Munda’s birth anniversary holds added significance as India concludes the nationwide celebration of Janjatiya Gaurav Varsh (2021–24).
- The declaration of Janjatiya Gaurav Divas marks the first national-level day devoted to tribal heritage and resistance.
- This recognition coincides with ongoing efforts to strengthen tribal welfare, infrastructure, and cultural revival.

Impact of Tribal Movements on India
- Collective Resistance: Tribal revolts such as those led by Tilka Manjhi, Sidhu–Kanhu, Rani Gaidinliu, and Tantia Bhil challenged colonial power, exploitation by moneylenders, and landlord domination.
- Cultural Defence: These movements protected indigenous customs, land rights, and community dignity.
- Political Awakening: Tribal uprisings laid the social foundations for later political consciousness and state formation.
Birsa Munda’s Legacy
- Leader of Ulgulan: Birsa’s revolt (1899–1900) mobilised Munda communities against land dispossession, forced labour, and missionary interference.
- Symbol of Identity: Revered as Dharti Aba, he promoted social reform and unity within the tribal society.
- National Recognition: His birth anniversary is officially observed as Janjatiya Gaurav Divas since 2021.
- Administrative Impact: Regions inspired by his movement eventually shaped the creation of Jharkhand and strengthened tribal representation.
Recent Government Measures for Tribal Empowerment
- PM-JANMAN Mission: Focuses on improving housing, connectivity, health, and education for Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs).
- Eklavya Schools: Over 700 EMRS sanctioned to expand quality residential schooling for tribal children.
- Cultural Protection: Tribal freedom fighter museums and heritage projects honour indigenous contributions.
- Market Integration: Initiatives to support tribal entrepreneurship and product marketing.
Conclusion
Birsa Munda’s legacy represents the ongoing fight for dignity, autonomy, and land rights among tribal communities. Recent welfare efforts and national recognitions show a growing commitment to their inclusion and cultural respect in India’s development path.
LITHIUM-RICH RED GIANTS AND HELIUM ABUNDANCE
TOPIC: (GS3) SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY: THE HINDU
A new study by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) has provided fresh insights into the internal structure and chemical evolution of red giant stars. Scientists have identified a clear spectroscopic association between lithium-rich red giants and higher-than-usual helium content.
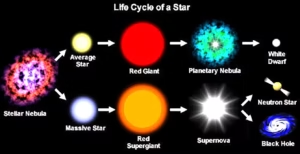
What Are Red Giant Stars?
- Evolved Stage: Red giants are stars that have used up hydrogen in their core, causing the core to shrink and the outer layers to swell dramatically.
- Physical Characteristics: Cooler surface (approx. 2,000–5,000 K). Much larger radius leading to high luminosity.
- Internal Processes: Hydrogen burning moves to a shell around the core, while the core heats until helium fusion begins.
- Position in Stellar Life Cycle: Represents the advanced evolutionary phase of medium-sized stars; even the Sun will reach this stage in the distant future.
- Final Outcome: They eventually shed their outer layers forming a planetary nebula, leaving a cooling white dwarf.
Outcomes of the IIA Study
- First Direct Link: The research established a clear correlation between helium-rich and lithium-rich red giants.
- Observational Basis: Data was collected from the Himalayan Chandra Telescope alongside global spectroscopic records.
- Sample Studied: 20 cool giant stars—18 red giants and 2 supergiants.
- Helium Enhancement: Six stars showed a high helium-to-hydrogen ratio (He/H > 0.1), mostly red giants.
- Scientific Interpretation: The findings suggest strong internal mixing and nuclear reactions that transport freshly created elements to the star’s surface.
Relationship Between Lithium and Helium
- Parallel Enrichment: All stars with unusually high helium were also lithium-rich, indicating a shared internal mixing pathway.
- Asymmetric Behaviour: However, some lithium-rich stars did not show increased helium, meaning lithium enhancement can occur independently.
- Internal Mixing: Deep convective currents inside red giants likely draw up lithium and helium produced in the inner layers to the outer atmosphere.
- Surface Evidence: These chemical changes, detected from the photosphere, act as indicators of stellar internal processes.
Why the Findings Matter
- New Measurement Achievement: This is the first time that surface helium levels in ordinary and lithium-rich red giants have been directly estimated.
- Advances Stellar Physics: Helps clarify how mixing, energy transport, and element formation work in red giant branch (RGB) stars.
- Galactic Evolution Impact: Enhances understanding of how such stars enrich the galaxy with heavier elements.
- Methodological Breakthrough: Improves indirect helium measurement techniques for cool stars, where helium lines are difficult to detect.
- Evolutionary Insight: Shows helium enhancement plays a key role in changes in brightness, temperature behaviour, and eventual mass loss.
NASA’S ESCAPADE MISSION TO MARS
TOPIC: (GS3) SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY: INDIAN EXPRESS
NASA has launched the ESCAPADE mission using Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket, marking an important milestone for commercial heavy-lift spaceflight.
About ESCAPADE Mission
- ESCAPADE consists of two small, identical Mars orbiters—named Blue and Gold—tasked with studying how the solar wind interacts with Mars’s upper atmosphere and patchy magnetosphere.
- Launch: Carried into space aboard New Glenn, showcasing the growing role of private launch vehicles in planetary exploration.
- Programme: Part of NASA’s SIMPLEx initiative, aimed at undertaking low-budget, small planetary missions through compact and efficient spacecraft.
- Scientific Objective: To explore how Mars gradually lost its thicker ancient atmosphere by observing charged particles, magnetic fields, and solar-wind-driven atmospheric escape.
- Trajectory: The mission takes an unconventional route, first travelling to the Earth–Sun L2 point for nearly a year before heading to Mars, with arrival planned for 2027.
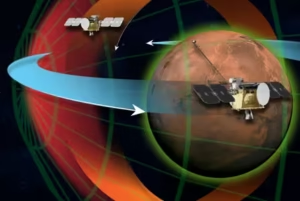
Features of ESCAPADE
- Dual-Spacecraft System: Operating together, the two orbiters allow scientists to distinguish temporal changes from spatial variations in Mars’s plasma environment.
- Magnetosphere Study: Since Mars lacks a global magnetic field, ESCAPADE will examine how its localized crustal magnetic patches interact with solar wind and how ions escape into space.
- Cost-Effective Design: Built on Rocket Lab’s Photon platform, the mission demonstrates a new model of affordable interplanetary exploration.
MARBURG VIRUS DISEASE
TOPIC: (GS3) SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY: PIB
The World Health Organization (WHO) has recently confirmed that Ethiopia has detected its first-ever outbreak of Marburg virus disease, raising public health concerns in the region.
About Marburg Virus Disease
- Nature of the Disease: Marburg virus disease (MVD) is a highly dangerous viral hemorrhagic fever, known for its severe symptoms and high fatality rate.
- Discovery: The disease was first recognized in 1967 in Marburg, Germany, following laboratory infections linked to imported African monkeys.
- Causative Agents: The illness is caused by two closely related viruses—Marburg virus (MARV) and Ravn virus (RAVV)—classified under the species Orthomarburgvirus marburgense.
- Natural Reservoir: The Egyptian fruit bat (Rousettus aegyptiacus) is believed to be the primary host in nature.
Transmission of Marburg Virus Disease
- Initial Transmission: Humans can contract the virus through prolonged exposure to fruit bat habitats or infected bat secretions.
- Human-to-Human Spread: The virus spreads between individuals through direct contact with the blood, bodily fluids, or tissues of infected persons, and through contaminated materials or surfaces.
- Regional Occurrence: Most recorded outbreaks have taken place in sub-Saharan Africa, with cases reported in Angola, Uganda, Tanzania, Ghana, Kenya, and Zimbabwe.
Symptoms of Marburg Virus Disease
- Early Stage: Patients typically develop sudden high fever, intense headaches, and severe fatigue.
- Progressive Symptoms: As the disease advances, individuals may suffer from extensive bleeding, liver impairment, multi-organ failure, and shock, often leading to death within a week of symptom appearance.
Treatment
- No Specific Cure: There is currently no approved antiviral treatment or vaccine for MVD.
- Supportive Care: Clinical management focuses on hydration, electrolyte balance, and treating secondary complications, which can significantly improve survival chances.
EXERCISE GARUDA 2025
TOPIC: (GS3) SECURITY: PIB
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is taking part in the 8th edition of Exercise Garuda, held in Mont-de-Marsan, France, alongside the French Air and Space Force (FASF). This remains one of the most important bilateral air engagements between India and France.

About Exercise Garuda 2025
- Bilateral Air Exercise: Garuda is a joint air drill conducted between India and France, aimed at strengthening defence cooperation and operational understanding.
- Objective: The primary aim is to improve air combat tactics, operational coordination, and mission planning in a realistic setting. The exercise helps both forces learn from each other’s operational experience and enhances interoperability.
- Indian Participation: The IAF has deployed Su-30MKI fighter aircraft, C-17 Globemaster III, and IL-78 air-to-air refuellers for the exercise.
- Operational Focus: During the drills, the Su-30MKI jets will fly alongside French multirole fighters in a range of simulated missions. These include air-to-air engagements, air defence missions, and coordinated strike operations designed to test crews under complex combat scenarios.
- Importance: The exercise provides a valuable platform for professional interaction, exchange of operational insights, and understanding of advanced aerial tactics. It also allows both air forces to observe each other’s best practices and strengthen long-term defence collaboration.
Other Joint Exercises with France
- Exercise Varuna: A bilateral naval exercise between the Indian Navy and the French Navy.
- Exercise Desert Knight-21: A joint air exercise involving frontline aircraft from both countries.
- Exercise Shakti: A bilateral Army exercise aimed at enhancing land-warfare cooperation.










